Planetary Conditions Nowcast
Near real-time values of Kp and Dst indices

The interaction between solar wind and the Earth's
magnetic field (Earth's magnetosphere) may lead to a
transference proces of matter and energy between these two
systems. This interaction can significantly modify the
shape, size and even the intensity of the Earth's
magnetosphere on a planetary scale during periods of hours
or days. These effects of the solar wind on the Earth's
magnetic field are known as geomagnetic
activity.
The effects
of geomagnetic activity will depend on the
characteristics of the interaction of the solar wind with
the Earth's magnetosphere. Geomagnetic activity regularly
affects the highest regions of the Earth's atmosphere. In
addition, geomagnetic activity can also negativelly affect
technology in space such as artificial satellites and
services associated with them such as telecommunications
and geopositioning services.
Due to the relevance geomagnetic activity has, scientists
have developed geomangetic indices. Geomagnetic indices
are tools whose objectives are to identify, describe,
classify and quantify geomagnetic activity, as well as its
characteristics. There are a number of geomagnetic
indices, and the calculation method for each of them
defines the phenomenon of the Earth's magnetic field that
it describes, as well as its characteristic cadence (time)
and region (latitude) of validity.
Space Weather National Laboratory (LANCE) uses the
geomagnetic indices Kp and Dst
for operational processes. Kp and Dst are tow of the International Association of
(IAGA)'s endorsed geomagnetic indices.
Kp - Nowcast
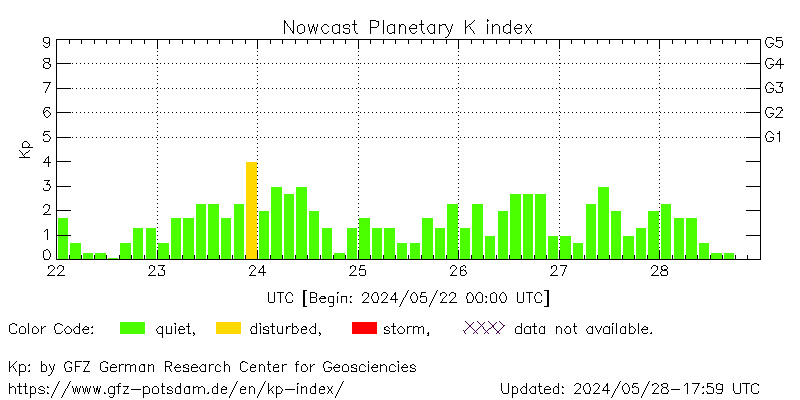
The Planetary-K index or Kp, broadly speaking,
characterizes the intensity of geomagnetic activity on a
planetary scale. However, due to the historical context at
the time of its creation, the Kp index measurement network
is heavily biased towards Europe and North America.
Additionally, because the measurement network of this
index is located in middle geomagnetic latitudes, its
values are highly conditioned to the geomagnetic activity
of these regions.
The Kp index measurement network is made up of 11 stations
located in the northern hemisphere and 2 in the southern
hemisphere. All of them located between 44° and 60° north
or south geomagnetic latitude.
Kp is the arithmetic mean of the standardized 3-hour K
indices for the 13 Kp observatories. Standardization is
achieved through standardization tables for each
observatory with the aim of eliminate UT and seasonal
variations in geomagnetic disturbances.
The GFZ website
dedicated to Kp and related geomagnetic indices, like ap.
The ap index is a linearization of Kp.
Text adapted from
Kp page at ISGI.
Dst - Near Real-Time
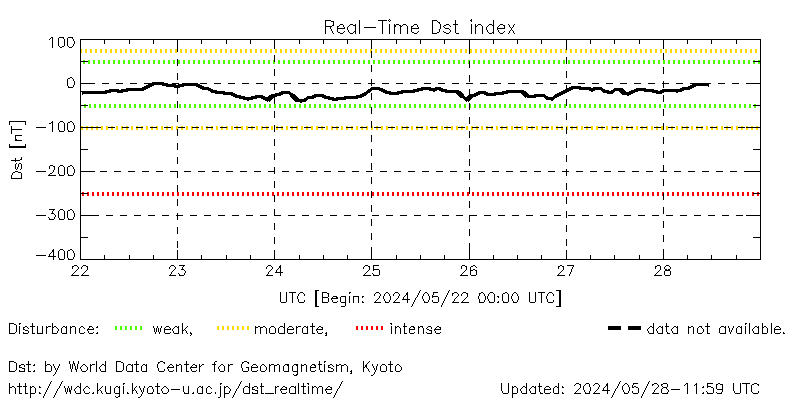
Disturbance storm-time index or Dst, aims to monitor the
axis-symmetric magnetic signature of magnetosphere
currents, including mainly the ring current, the tail
currents and also the magnetopause Chapman-Ferraro
current.
The network to compute Dst index is made of 4 low latitude
magnetic observatories distribuited arround the globe. The
observatories are sufficiently distant from the auroral
and equatorial electrojets to inhibit noise from these two
sources.
Dst is computed using 1-hour values from each one the four
observatories. In each observatory a local Dst values are
computed using the following protocol:
(i) contributions to horizontal field (H)
from the background field (non-transient field of core and
crustal origin) and the solar regular daily variation are
subtracted from the observed value of H ; (ii)
the so-obtained residual (ΔH) is normalized to the dipole
equator thorugh the geomagnetic latited in which each
observatory is located at; (iii) for
each 1-hour UT interval, the Dst index is the average of
the local Dst hourly mean values at the four
observatories.
Dst values are publisched in real-time by WDC
for Geomagnetism - Kyoto, Japan.
Text adapted from Dst
page at ISGI.
